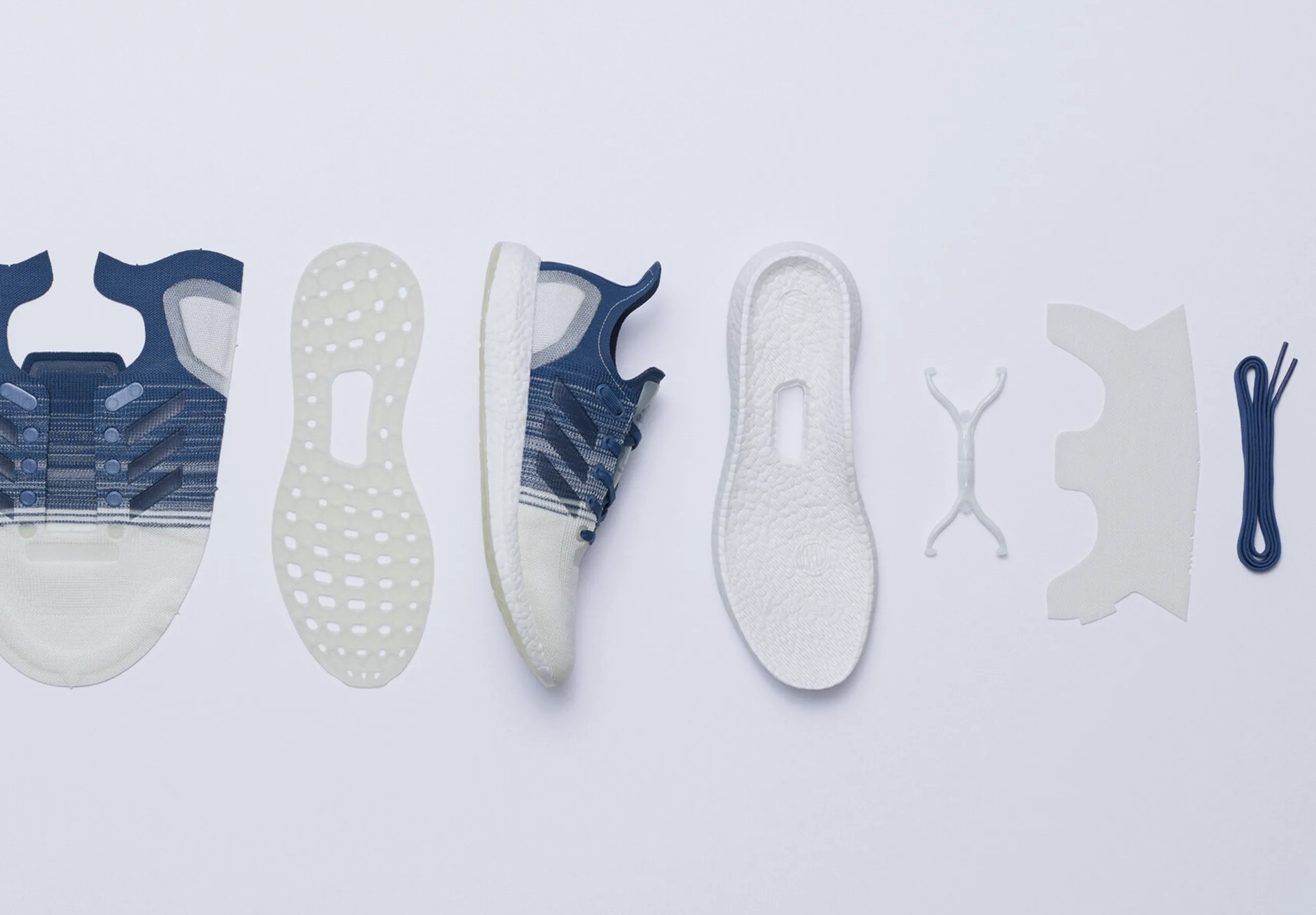
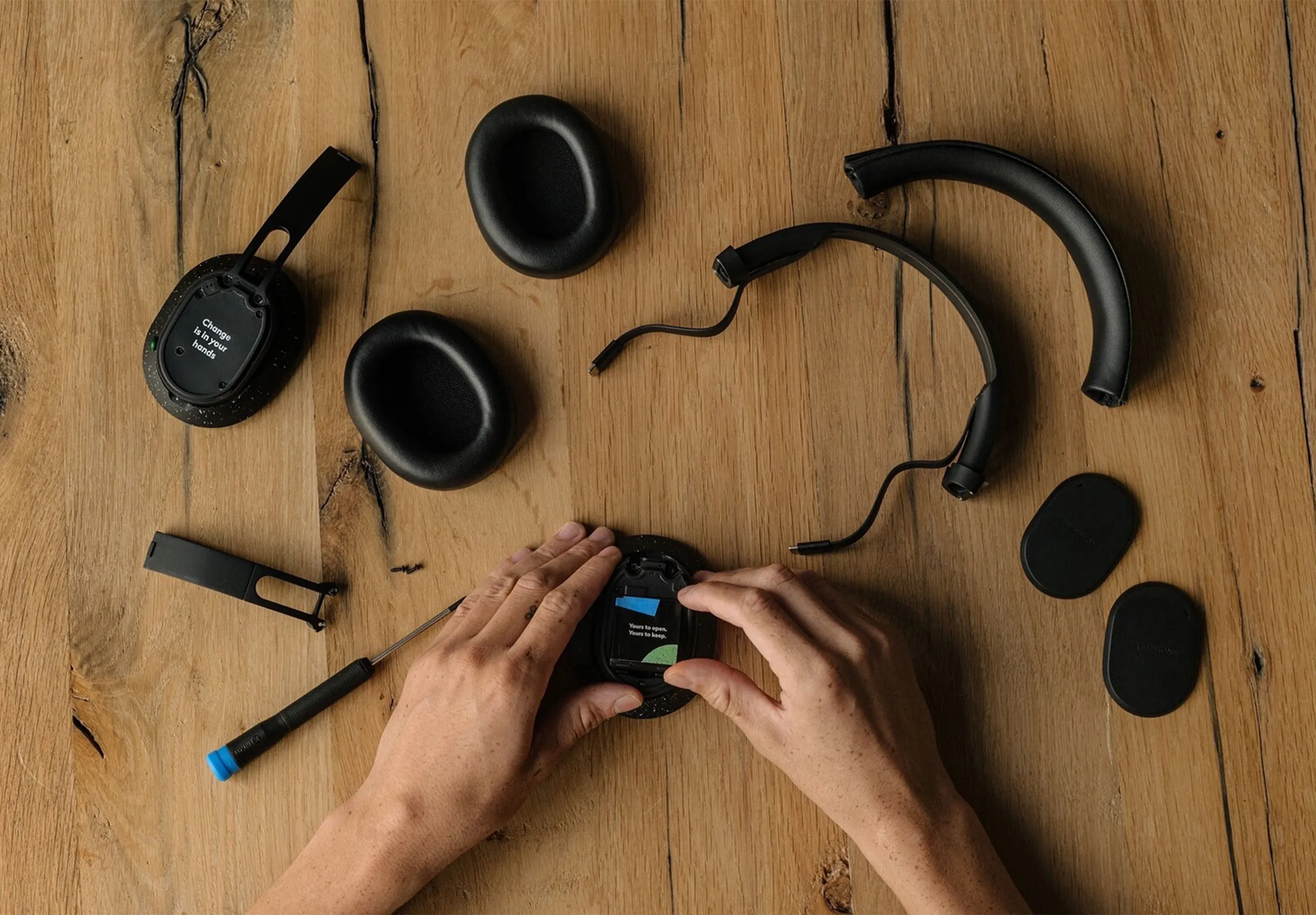
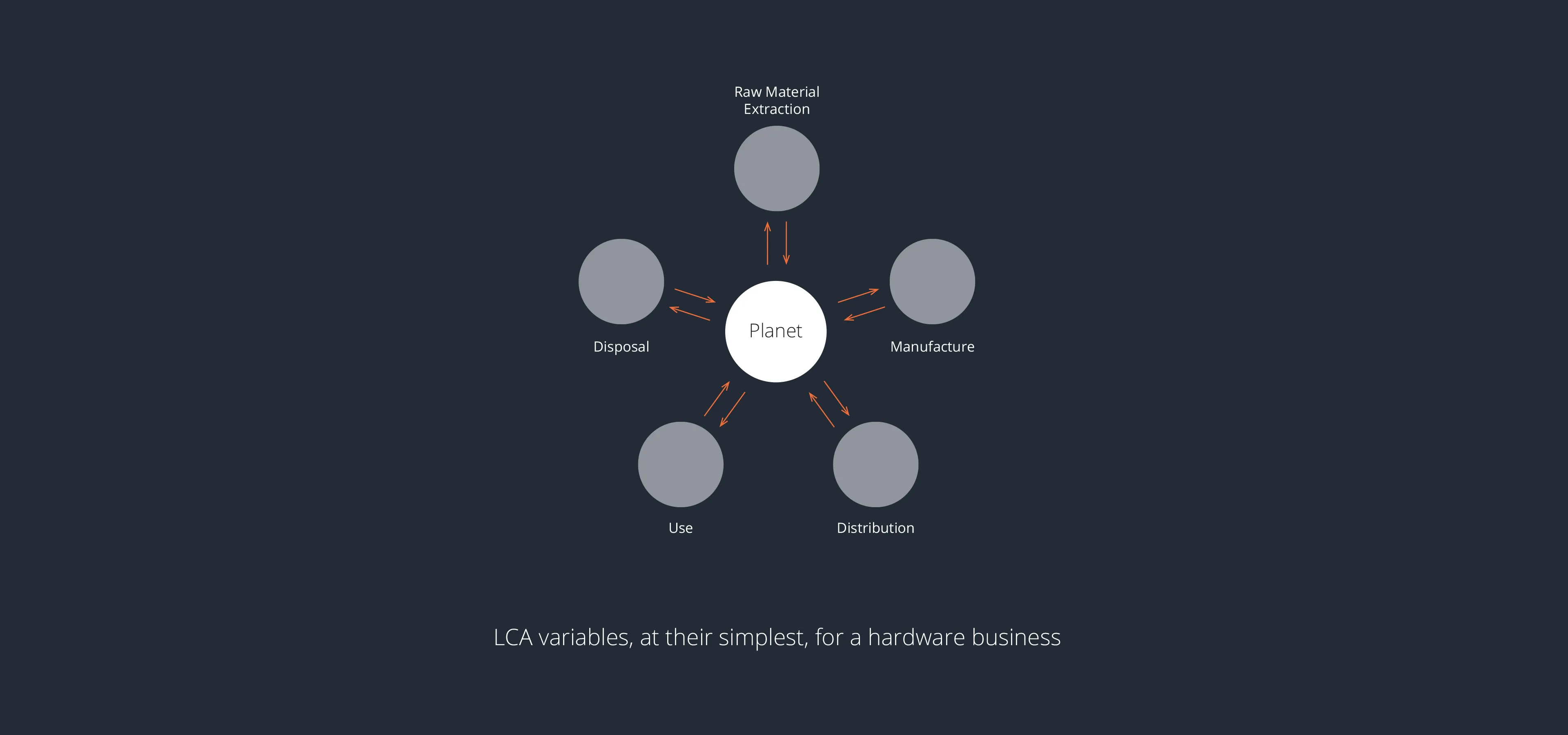
Carbon Recalibration
Design shapes impact. The earlier sustainability is embedded into product development, the greater the potential for lasting change. But wherever you are in the process, targeted interventions can shift the dial.
In this piece, we share core ecodesign principles, explore the balance between data and intuition, and introduce our new Carbon Recalibration service.
Let us know what you think.
Short on time? Use these links.
Balancing data and intuition
When it comes to reducing a product’s environmental impact, starting at the beginning of development is, of course, the easiest and most effective approach.
However, even mid-program interventions can drive meaningful change. Successful environmental initiatives (and – let’s face it, most brands are still working on essential carbon reduction) must go beyond one-off interventions. Like the design-thinking approach, effective sustainability efforts are adaptive and iterative: observe, ideate, prototype, test, and repeat.
From our experience working with diverse clients on challenging product briefs, we have learned how crucial it is to balance data-driven decisions with intuitive design interventions.
Designers bring a unique perspective to sustainability by anticipating real-world use, balancing competing priorities, and spotting lifecycle opportunities beyond the data. Intuition supports bold ideas, rapid decisions, and holistic thinking—especially valuable when data is limited or timelines are tight.
Design-led interventions for carbon reduction
Eco-design best practices—from industrial design through design for manufacturing—play a crucial role in impact reduction, creating opportunities for powerful interventions such as:
1. Reduce
Drastically reducing those life cycle peaks might be harder than you think. Typically, the biggest spikes fall outside the traditional design remit, residing instead in supply chain, production or use phase activities.
While design teams can of course advocate and provide agency across the wider business for ethical supply chain evaluation, doubling down on ‘reduction’ must be our mantra during the design phase.
Focus on material and material energy impact material reduction – from part weight, to reducing material diversity and reduction of virgin material content are all areas that should be front of mind.
2. Increase longevity and repair
Whilst longevity and repair are often cited as the eco-design champions, the use phase of your product’s lifecycle is often the greatest contributor to environmental impact. Smart brands need strategies (and beautifully designed experiences) around ‘environmental breakeven’ — identifying when replacing a product creates less environmental impact than maintaining an older one.
This scenario typically occurs when technological advancements have significantly improved efficiency since the product’s initial launch. Even better if the old product can be remanufactured rather than merely recycled, further reducing waste impact and conserving embodied energy.
3. What’s better than repair? Maintenance
Designing simple maintenance initiatives to help avoid repair is a great way for some product categories to increase their lifetime value longevity and minimise the inevitable energy impact associated with the production and shipping of a product for repair.
If repair is necessary, consider whether your product could be serviced without a back to base return – after all, the energy cost of shipping a single replacement part is far less than transporting the entire product back and forth.
4. Let’s be honest: recycling is still waste
Consider if all, or part, of your product could be remanufactured rather than recycled. Remanufacture (although challenging) recoups inefficiencies associated with end of life (collection, disassembly, waste processing etc.) and should be considered where viable.
5. Material selection
Selecting appropriate materials is crucial, as seemingly “sustainable” materials vary in their environmental impact. Balancing cost, aesthetics, durability and process suitability is essential to prevent high impact material use.
For example, combining recycled and bio-based materials can reduce impact at your product’s end-of-life recyclability – but this might have other negative environmental impacts. Bio-based resins can reduce emissions in one area, but increase environmental impacts in others such as land and water use and might therefore reduce product longevity.
Carbon Recalibration with Rodd
Ultimately, the journey toward more sustainable products requires both a strong team and a clear strategy.
Carbon Recalibration is the term we’ve coined for our approach to helping in-house teams optimise impact reduction and accelerate the implementation of eco-design guidelines.
It’s the perfect solution for teams already on this journey—perhaps with a small design-led sustainability group who’ve conducted internal LCA analysis—but now need specialist expertise to accelerate change from both environmental and brand perspectives.
We work alongside these businesses to accelerate the iteration of design alternatives and LCA recalculation. Our design and material expertise allows a greater exploration of potential impact reduction scenarios whilst you re-run the numbers.
Hard data is the backbone of effective carbon recalibration. It provides a foundation for establishing baselines, measuring progress, and ensuring that design interventions have a real impact.
Ready for your next step?
Depending on where you are in your carbon reduction journey, we offer a range of services to support your efforts:
Ideal for teams starting out, providing a comprehensive LCA Impact Report to measure your product’s carbon emissions against a predefined matrix.
Perfect for those ready to implement and measure design-led carbon reduction initiatives.
If you need rapid insights, our Carbon Realtime service offers fast, expert-led analysis of potential design for high-impact teams needing quick, informed decisions.
Ready to drive market disruption? We offer a one-day workshop for multi-stakeholder teams seeking a strategic roadmap for systemic change.
Tomorrow’s advantage lies with design-led brands that embrace meaningful change.